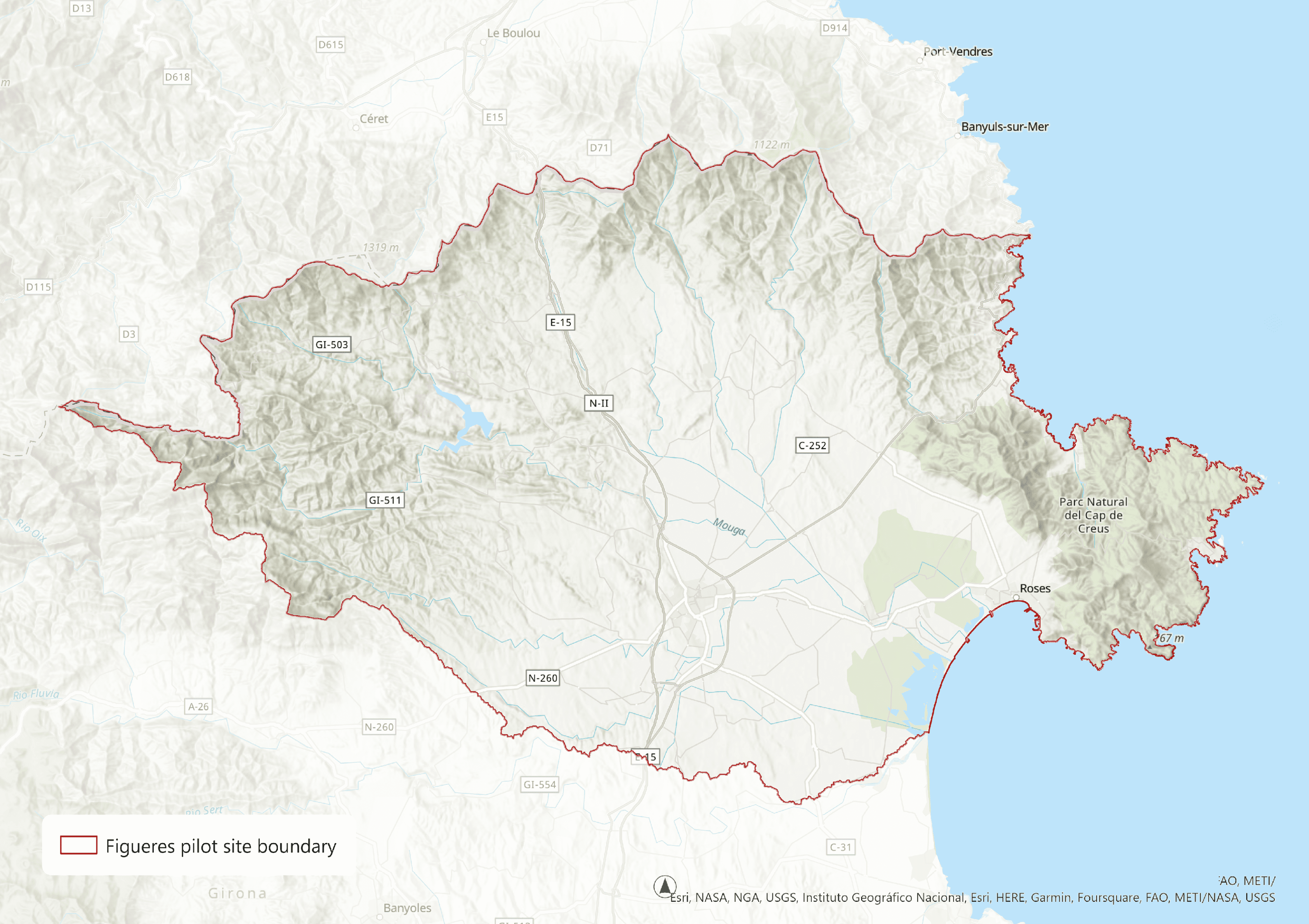
PS#3: Figueres (SP)
This page is also available in Spanish ![]()
Led by EUT and FIGUERES


Description of the area
Figueres is the county capital of the Alt Empordà (68 municipalities which a total population of 136,000 (2021) in the North-East of Spain. Figueres, has a population of just over 47,000 (2021) living in an area of 19.2 km2. Principal economic activities in the county are commerce, agriculture and tourism.
84% of the water for Figueres comes from the reservoir of Boadella (fed by the river Muga) and 16% from groundwater wells. The water is of an extremely high quality. The principal challenge is drought exasperated by the unusually high demand during the summer months as a result of a high level of tourism and the irrigation needs of local agriculture to produce fodder for cattle, pigs and sheep, (the principal agricultural use of water in the county), mixed crops and to a much lesser extent, vineyards and olive trees.
Wastewater and rain water are not separated in most of the sewer network, and once treated at the WWTP is released into the River Muga via the Mal Pas Canal, which in turn enters the Mediterranean in the Bay of Roses, as does the other county river, the Fluvia which does not supply water to Figueres.
Main water governance challenges
Figueres has a typical coastal Mediterranean climate, with mild winters and hot, often humid summers. Despite the humidity, and as is the case in many Mediterranean regions, water scarcity is the primary challenge facing the pilot site.
During the hottest months of the year, June, July and August, 10,000m3 are consumed a day. If the rains fail in January, February and March, there are severe supply problems exasperated by the fact that one of the principal economic activities of the county is tourism. Figueres itself, receives more 1 million visitors a year to the Dali Museum and the surrounding area situated on the border with France is a key touristic area for Catalonia.
A general awareness regarding the issue of water exists when there is an extreme event such as the prolonged drought of 2007-2008. However, over a period of time, the interest on the part of the general public wanes, once restrictions are lifted. Despite certain efforts in the period 2007 and 2011, the relationship between Figueres and its neighbouring municipalities does not always result in a coherent overall approach to the administration of the Muga fluvial system.
Furthermore, it is the responsibility of the Agencia Catalana d’Aigua of the Government of Catalonia to designate the proportions of water allotted to the agricultural sector, tourism (the coastal municipalities) and Figueres and the inland towns and villages.
Key stakeholders
The principal stakeholders to be involved in InnWater are the Quintuple Helix at a local level, the municipal government, the Ajuntament de Figueres, the water and transport utility controlled by the City Council, named FISERSA, the Catalan Water Agency, (Agencia Catalana d’Aigua ACA) and local environmental interest groups, the most important of which is called IAEDEN. The Environment Network of the Urban Area of Figueres (Xarxa Medioambiental de l’Area Urbana de Figueres) which is composed of Figueres and 16 other municipalities will also be involved as will the Alt Empordà County Council. (Consell Comarcal d’Alt Empordà).
InnWater governance innovation and Solutions to be experienced
A greater transparency between sectors and trans-sectoral cross-cutting approaches which will involve both the Quintuple Helix at a socio-political level and the WEFE Nexus at a technical planning level to allocate water resources within the river basin of the Muga will be achieved by the creation of the RBWF and the reinforcement at a local level of the Environment Network of the Urban Area of Figueres which will create the bridge between the different levels of governance and all stakeholders at a municipal, county and regional level.
The Water Governance Diagnostic Tool will be employed in order to create observe and monitor further progress throughout InnWater and aspects of the Governance Toolbox employed and tested.
Recommendations regarding policy, regulations and economic factors will collated in a publication in both English and Catalan to create a more effective governance structure which at the same time reflects the importance of the interaction of water with energy, food and the ecosystems within the area. Citizen and professional awareness will be raised. Citizen participation will increase by 20% and the input of all genders, low-income groups, ethnic minorities, age groups and the physically challenged will increase by 50%.
At the conclusion of InnWater, the 16 municipalities of the Urban Area of Figueres will have also joined the RBWF and in the province of Girona (in which Figueres is the second city) two other RBWFs based on the Rivers Fluvia and Ter will have also been initiated to be supported by the Social Engagement Platform of the United Nations World Water Quality Alliance.